The point is composed of the volume flow Q and the flow rate H.
To calculate the design point, the required volume flow (flow rate of the pump) is first determined. Depending on the application, this can depend on various variables (e.g. heat requirement for heating systems, volume of wastewater produced, etc.). The calculated volume flow is then used to determine the frictional losses of the pipeline, which together with the static head then gives the total head of the pump.
If a minimum flow velocity is specified for the application and this is not reached for the calculated flow rate, the rated flow rate is adjusted so that the minimum flow velocity is reached. The pump then runs in off mode (intermittent).
The duty point of the system is the required operating point for the pump selection. The standard pumps usually have a deviation between the desired duty point and the actual operating point. The permissible deviation depends on the field of application and is partly regulated by applicable standards.
With speed-controlled pumps, the speed of the pump is modified so that the set operating point is approached exactly. Especially in systems that are operated in different load conditions (e.g. heating system), this enables efficient operation.
Depending on the design of the pump, there are further possibilities for adapting the pump performance curve to the duty point. In addition to changing the speed, the following methods are widely used:
- Impeller trimming
- Blade angle adjustment for axial flow pumps
- Throttling
- Bypass
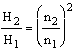 3. Model law
3. Model law
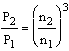 Q – flow rate
H – delivery head
P – power consumption
n – speed
The indices relate to the respective speed.
The affinity laws apply exactly to frictionless, incompressible flows. For technical applications, they are to be regarded as an approximate solution.
In general, these affinity laws are independent of how the speed change is technically implemented. Traditionally, multi-speed functions of small and medium size pumps are realized by changing the motor windings configurations to achieve stepped speed variations. Meanwhile, these have been largely replaced by frequency converters.
Slow-running electric drives are very expensive for larger centrifugal pumps, so that reduction gears are used for these cases.
Combustion engines are used for some mobile applications. They are also variable in speed within a specified range.
Q – flow rate
H – delivery head
P – power consumption
n – speed
The indices relate to the respective speed.
The affinity laws apply exactly to frictionless, incompressible flows. For technical applications, they are to be regarded as an approximate solution.
In general, these affinity laws are independent of how the speed change is technically implemented. Traditionally, multi-speed functions of small and medium size pumps are realized by changing the motor windings configurations to achieve stepped speed variations. Meanwhile, these have been largely replaced by frequency converters.
Slow-running electric drives are very expensive for larger centrifugal pumps, so that reduction gears are used for these cases.
Combustion engines are used for some mobile applications. They are also variable in speed within a specified range. 
