Design
The uniform feature of glanded pumps is the separation between the pumped fluid and theirst drive motor. The connection between the impeller in the pump body and the motor is made by either a common shaft or by coupled shaft parts. The rotating motor component remains dry (thus the term Dry-Motor Pump). The rotor support by means of roller bearings requires separate lubrication. The pumps are normally driven by IEC-standards electric motors but also by special design motors up to explosion-protected versions.
Pump types / function
Glanded pumps are of two distinctly different designs:
- Monobloc Glanded Centrifugal Pumps
- DIN-Standards Centrifugal End-Suction Pumps
Glanded pumps are louder than glandless pumps. The noise is caused by the roller bearing (ball bearing or needle bearing) and the fan wheel of the surface-cooled electric motor. The noise of the pump itself – flow noise, bearing noise – is completely negligible, unless unusual operating situations occur (cavitation, etc.).
There are two distinctive designs of glandless pumps, one with dry stator windings (Canned Rotor Motor) and one with wet-stator windings (Wet Stator Motor).
With this design, there is no shaft seal between the pump and the motor. The pumped medium is used for cooling and lubricating the motor at the same time. Glandless pumps are considered to be particularly low-noise, which makes them ideal for use in living spaces. The omission of the shaft seal makes the system particularly low-maintenance and leakage-free. This also makes canned motor pumps interesting in process technology for applications where leakage-free pumping is important.
A disadvantage is the lower efficiency compared to pumps with shaft seals (glanded pumps), especially at higher outputs.
Typical applications for canned rotor pumps are as heating circulating pumps, process pumps for the chemical industry and process engineering and as nuclear reactor pumps. Wet stator pumps are mainly used as submersible pumps in wells and for circulating duties in conventional power plants.
They are mainly used in installations requiring large flow rates, abnormally high working pressures (cast steel, S.G.iron) or special temperatures or pressures respectively. Their installation requires heavy foundations and extensive piping configurations. The high flow velocities within the pump body and the pump ports often require special noise attenuation measures.
The following diagram depicts a sectional view of a flexibly-coupled end-suctionpump without motor, coupling and baseplate.
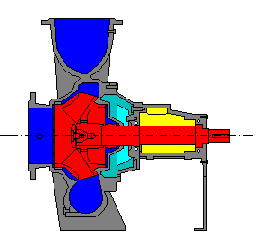

The pumps can be directly pipe mounted or, if necessary, be separately supported by foundations or brackets.
The high continuous temperature rating (up to 140°C) and the vibration-free operation on account of respectively shaped pump housings, impellers and drive motors are the decisive design features of this, especially for building services developed pump design. Low flow velocities through the housing as well at the pump ports make special noise attenuating measures (flexible connections) superfluous.
In building services, especially for pumps for heating and air-conditioning technology, the classification of the pump design according to the sealing (wetting of the motor) is widespread:
| Design |
Description |
| Glandless Pump |
Glandless pump with canned rotor motor |
| Glanded Pump |
Centrifugal pump with shaft seal |
In addition, the subdivision according to the type of installation or the arrangement of the drive is common:
- Monobloc with flange-mounted motor
- DIN-standards with motor and coupling on common baseplate


