- Monobloc Glanded Centrifugal Pumps
- DIN-Standards Centrifugal End-Suction Pumps
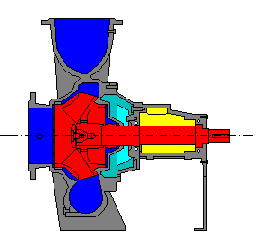
Glanded Pump
Design
The uniform feature of glanded pumps is the separation between the pumped fluid and theirst drive motor. The connection between the impeller in the pump body and the motor is made by either a common shaft or by coupled shaft parts. The rotating motor component remains dry (thus the term Dry-Motor Pump). The rotor support by means of roller bearings requires separate lubrication. The pumps are normally driven by IEC-standards electric motors but also by special design motors up to explosion-protected versions.
Pump types / function
Glanded pumps are of two distinctly different designs: