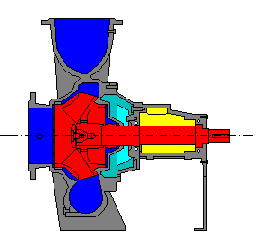
- bi-directional function
- flexible shaft attachment by means of an elastomeric bellows (automatic compensation of seal seat wear by means of the integrated spring)
- hard/soft material combination (ceramics or hardened metal to carbon) offering optimum lubricating qualities
- attachment to a bronze or stainless steel shaft sleeve.
Shaft Seals
The two most common systems are:
The stuffing box – the conventional shaft seal – is, due to its intense maintenance requirements, only rarely used for building services application and then mostly in conjunction with flexibly coupled baseplate pumps. Their use with Inline pumps is restricted to some special design versions.
Specific operating conditions require distinctly different types of glanded seals. They are subject to constant observation and maintenance adjustments. Proper lubrication of the gland packing requires a certain leak-age rate which at average working pressures/temperatures and normal water quality amounts to a mean rate of 10 drops per minute. Special manufacturers’ recommendations are to be observed individually. Service life expectancy is between 1 and 2 years, this can sometimes extend to several years on favourable operating conditions. Extremely bad water conditions (sediments, additives, overheating) can however drastically cut short their service life.
Glanded seals should preferentially be used in conjunction with shaft sleeves in order to avoid damage to the shaft by aggressive fluids or due to inproper treatment of the glanded packing respectively.
The maintenance-free mechanical seal has virtually become standard equipment for glanded pumps in building services and many other applications.
They operate without any visible water leakage and do not require any maintenance whatsover during their service life, which runs between 1 and 2 years, maximum 3 years. However, extremely bad water (sedi-ments, use of additives, overheating) can also severely shorten their service life. In such cases it is advis-able to check their suitability or the necessity for special designs with the seal manufacturers.
The following mechanical seal configurations have proved to be the most suitable for building services: