Xylem and ESRI: Innovative AI Pipeline Analysis Model
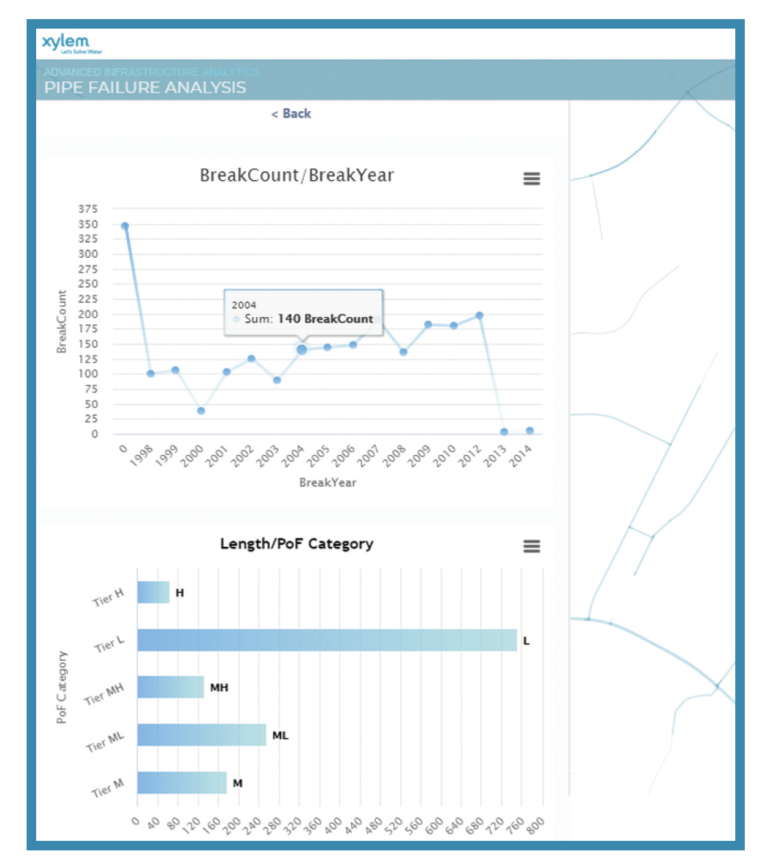
Using machine learning to predict pipe failures (Image source: Xylem Inc. / Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.)
The model, one of the first in North America to reliably predict future pipe failures, uses an AI-based solution from Xylem to analyze data within the utility’s Esri ArcGIS Enterprise system, such as breaks and other infrastructure data, combined with open source information in the analysis.
“Xylem is committed to driving innovation in the water sector, and partnering with other best-in-class technology leaders like Esri helps us further accelerate water innovation,” says Dave Ayers, VP Innovation Strategy & Partnerships at Xylem. “Together we help water operators and other users of water make their communities more water-secure and resilient.”
Using machine learning to predict pipe failures
The water utility, which takes a proactive approach to continuously improving service reliability for its 270,000 customers, was facing an all-too-common situation – aging water infrastructure. With more than 1,000 miles of water mains across their system, and an average pipe age of about 50 years, the utility was experiencing water main breaks at an ever-increasing rate. This prompted them to seek innovative strategies that would improve service reliability while minimizing repair and replacement costs.
With water main breaks increasing, utility customers were experiencing unpredictable service outages, costly repairs, and highly disruptive road closures. To improve its reputation and customer service, the utility wanted to be more proactive in its water infrastructure management and prioritize pipes that needed the greatest attention.
“Our goal is to leverage machine learning to identify variables that could lead to pipeline failure, and as an outcome, support our capital improvement planning,” says the utility’s Project Manager at the Department of Public Works.
Developing a risk model with artificial intelligence
The utility had previously worked with Xylem to manage their PCCP (prestressed concrete cylinder pipe) inventory. Based on Xylem’s deep expertise in identifying water main preservation strategies and Xylem’s close partnership with Esri for more than 20 years, the utility engaged Xylem in 2014 to develop a risk model with artificial intelligence that could be validated, updated and displayed through Esri’s ArcGIS system for their team’s continuous use.
The utility and Xylem then worked together to implement a quantitative risk model combining probability of failure (when a pipe will most likely fail) with the consequence of failure (the social, financial and environmental costs of the failure). Xylem’s machine learning solution forecasts the probability of when each water main in the system might fail using multiple data inputs including results from prior condition assessments. As more data is collected over time and changes are made to the system, the GIS and machine learning algorithms are updated to give a continuous understanding of the overall health of the system.
Xylem and Esri’s solution reliably predicts future failures
This AI pipeline analysis model is one of the first artificial intelligence water main break models in North America to reliably predict future failures in the distribution system. The model uses data within the utility’s ArcGIS enterprise system from Esri, such as breaks and other infrastructure data, combined with open-source information in the analysis. This data-driven approach provides substantial advantages over traditional subjectively scored models where outputs often remain static even when inputs are updated.
“Water utilities can significantly reduce costs and make their communities more resilient by combining ArcGIS with Xylem’s innovative AI-based pipe failure analysis,” says David Wachal, Director, Esri Global Water Practice.
Xylem’s risk model is able to update results as new information is collected from the system, including main breaks, pipeline condition and other operational data. Results allow clients to prioritize and stage pipeline replacement, lowering costs and reducing customer impacts by targeting the most critical and deteriorated pipes.
To validate this approach, and reduce the overall probability of failures, the utility selected a forecasted “hotspot,” or area with a high number of breaks, to pilot Xylem’s machine-learning technology to reduce the overall probability of failure.
Additionally, Xylem provided a mobile field event tracking application (capturing information on pipe breaks) for the utility’s field operators. This value-added feature not only increased the accuracy of break data records, it also reduced the overall labor time required to update their CMMS and GIS, and improved pipe failure predictions.
$70 million in savings and a dramatic reduction in pipe failures
The success of the pilot program has led the utility to develop additional cost-effective pipeline renewal strategies using an AI-based risk model. Once implemented across the entire distribution system, this model can help the utility lower their annual costs related to pipeline replacement from $90 million to just $20 million, or 77 percent, while achieving a dramatic four-fold reduction in failures.
“We’re proud to team with Esri to deploy innovative solutions that will truly change how water utilities can predict pipe failures and prioritize repairs,” says Dave Ayers from Xylem. “By partnering with water operators to drive innovation, and bringing together the collective power of our expertise and technologies, we’re accelerating progress and developing bold new approaches to help solve the greatest water challenges of our time and create a more sustainable world.”
Source: Xylem Inc.







